Use Google Sheets AI Formulas to Automatically Process Saved Data
Google Sheets now includes a built-in =AI() formula powered by Gemini that can classify data, analyze sentiment, summarize text, extract details, and more — directly inside your spreadsheet cells.
When you combine this with Add to Sheets, you get a powerful workflow: save raw data from any website, and let AI formulas automatically process it in adjacent columns. No manual cleanup. No switching between tools.
Important: AI Formulas Are a Google Sheets Feature
The =AI() function is built into Google Sheets by Google — it’s not part of the Add to Sheets extension. To use it, you need an eligible Google Workspace plan or Google AI plan from Google.
Add to Sheets handles the data collection side — getting information from websites into your spreadsheet quickly. Google’s AI formulas handle the data processing side — automatically analyzing and enriching that data once it’s in your sheet.
They work independently but are powerful together.
How the Workflow Works
- Set up your sheet with columns for raw data and AI-processed results
- Save data from websites using Add to Sheets (right-click save or Quick Row Entry)
- AI formulas run automatically on each new row, filling in classification, summaries, and extracted details
The key insight: you don’t need to save perfectly structured data. Save messy text, descriptions, or entire paragraphs — the AI formulas clean it up and extract what matters.
Example Workflows
Lead Qualification from LinkedIn
Save prospect info from LinkedIn profiles using Quick Row Entry, then let AI formulas qualify them.
| Name | Headline | About (raw text) | Industry | Seniority | Relevant? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jane Smith | VP Marketing at Acme | 15 years in B2B SaaS… | =AI(“what industry?”, C2) | =AI(“seniority level?”, B2) | =AI(“is this person a decision maker for software purchases? yes or no”, B2:C2) |
Columns you save with Add to Sheets: Name, Headline, About text, Profile URL Columns AI fills automatically: Industry, Seniority Level, Relevance Score
With Quick Row Entry, you open a form, paste the name, headline, and about section, submit — and the AI columns populate on their own.
Product Research from Amazon or eBay
Save product details from Amazon or eBay, then let AI categorize and compare.
| Product | Description (raw) | Price | Category | Key Features | Buy Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bluetooth Speaker XYZ | Portable, waterproof, 20hr battery… | $45 | =AI(“product category?”, B2) | =AI(“list top 3 features”, B2) | =AI(“is this good value under $50? brief answer”, B2:C2) |
You save: Product name, description, price AI fills: Category, key features summary, value assessment
Review Sentiment from Yelp or Google Maps
Save business reviews from Yelp or Google Maps, then let AI score them.
| Business | Review Text | Sentiment | Key Issue | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Joe’s Pizza | “Great crust but waited 45 min…” | =AI(“positive, negative, or mixed?”, B2) | =AI(“main complaint if any?”, B2) | =AI(“summarize in 10 words”, B2) |
Job Fit Analysis from Indeed or Glassdoor
Save job listings from Indeed or Glassdoor, then let AI evaluate fit.
| Job Title | Description (raw) | Your Skills Match | Key Requirements | Remote? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senior Developer | Must have 5+ years React… | =AI(“does this match: React, Node, Python?”, B2) | =AI(“list required skills”, B2) | =AI(“is this remote, hybrid, or onsite?”, B2) |
Paste your skills list once in a reference cell, then use AI formulas to compare every job description against it automatically.
Content Research from Reddit
Save discussion threads from Reddit, then let AI categorize and extract insights.
| Post Title | Comment Text | Topic | Sentiment | Actionable Insight |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| “Best tools for…” | “I switched to X because…” | =AI(“topic category?”, B2) | =AI(“sentiment?”, B2) | =AI(“what product feedback is here?”, B2) |
Email Triage from Gmail
Save email content from Gmail, then let AI prioritize.
| From | Subject | Body (raw) | Priority | Action Needed | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [email protected] | Re: Q1 proposal | Thanks for sending… | =AI(“priority: high, medium, low?”, C2) | =AI(“what action is needed?”, C2) | =AI(“summarize in one sentence”, C2) |
Why Quick Row Entry Makes This Work
The magic of this workflow is Quick Row Entry (a Pro feature).
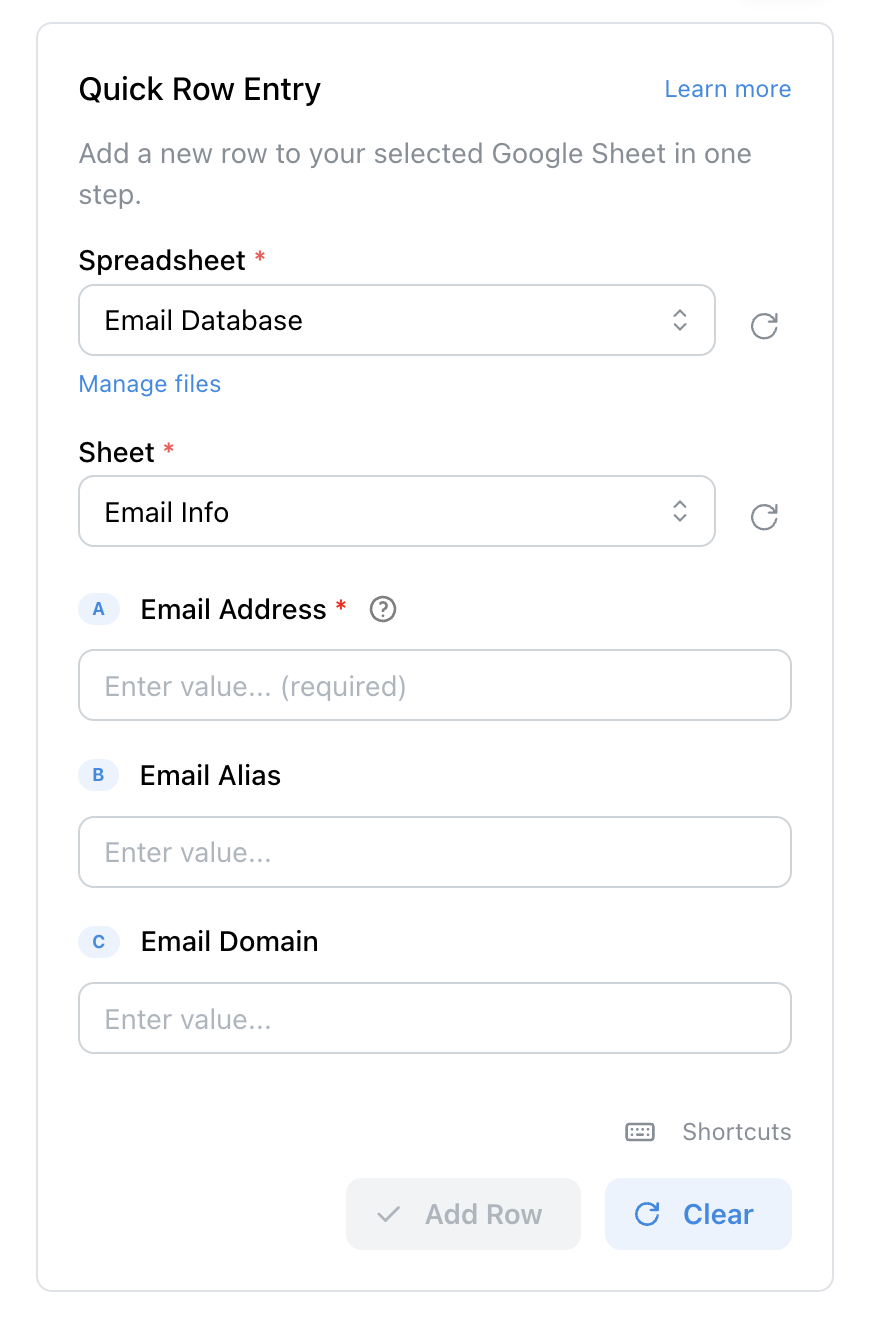
Quick Row Entry lets you paste raw data into a form and save an entire row at once
Instead of carefully selecting and saving individual fields from a website, you:
- Open the Quick Row Entry form
- Paste raw, messy data — an entire product description, a full LinkedIn about section, a block of review text
- Submit
The AI formulas in your sheet do the rest. They parse the raw text, extract the structured details, classify it, and summarize it. You don’t need to save clean, structured data — just get it into the sheet and let AI handle the cleanup.
This means you need more columns (raw data + AI-processed results), which is where Add to Sheets Pro’s unlimited columns become essential. A typical AI-enhanced sheet might have 4-5 columns you fill in and 3-5 more that AI populates — well beyond the free plan’s 5-column limit.
Tips for Better AI Formula Results
Be Specific in Your Prompts
Vague prompts get vague results. Compare:
- ❌
=AI("analyze this", B2)— too open-ended - ✅
=AI("is this a B2B or B2C company? answer with just B2B or B2C", B2)— specific, constrained output
Constrain the Output Format
Tell the formula exactly what format you want:
=AI("rate sentiment 1-5 where 1 is very negative, answer with just the number", B2)=AI("list the top 3 skills mentioned, comma separated", B2)=AI("yes or no: does this mention remote work?", B2)
Pass Multiple Cells for Context
You can pass a range so the AI formula sees multiple columns at once:
=AI("is this job a good fit for someone with React and Python skills?", A2:C2)— passes job title, description, and requirements together=AI("summarize this product and whether the price is fair", A2:C2)— passes product name, description, and price together
Or build the context directly into the prompt:
=AI("is "&A2&" a good fit for a senior developer role?")— references a specific cell inline within the prompt
Use a Reference Cell for Repeated Context
Instead of repeating long prompts, put your criteria in a cell and reference it inline:
- Cell D1: “React, Node.js, Python, 5+ years experience”
- Formula:
=AI("does this job description match these skills: "&$D$1&"? yes or no", B2)
Copy the formula down and every row references the same criteria cell in the prompt, with the job description passed as the range.
Pair with Automations and Custom Values
If you’re on the Automations plan, you can use no-code automations to extract structured data from web pages before it even hits your sheet. The automation handles extraction, and AI formulas handle analysis — two layers of automatic processing.
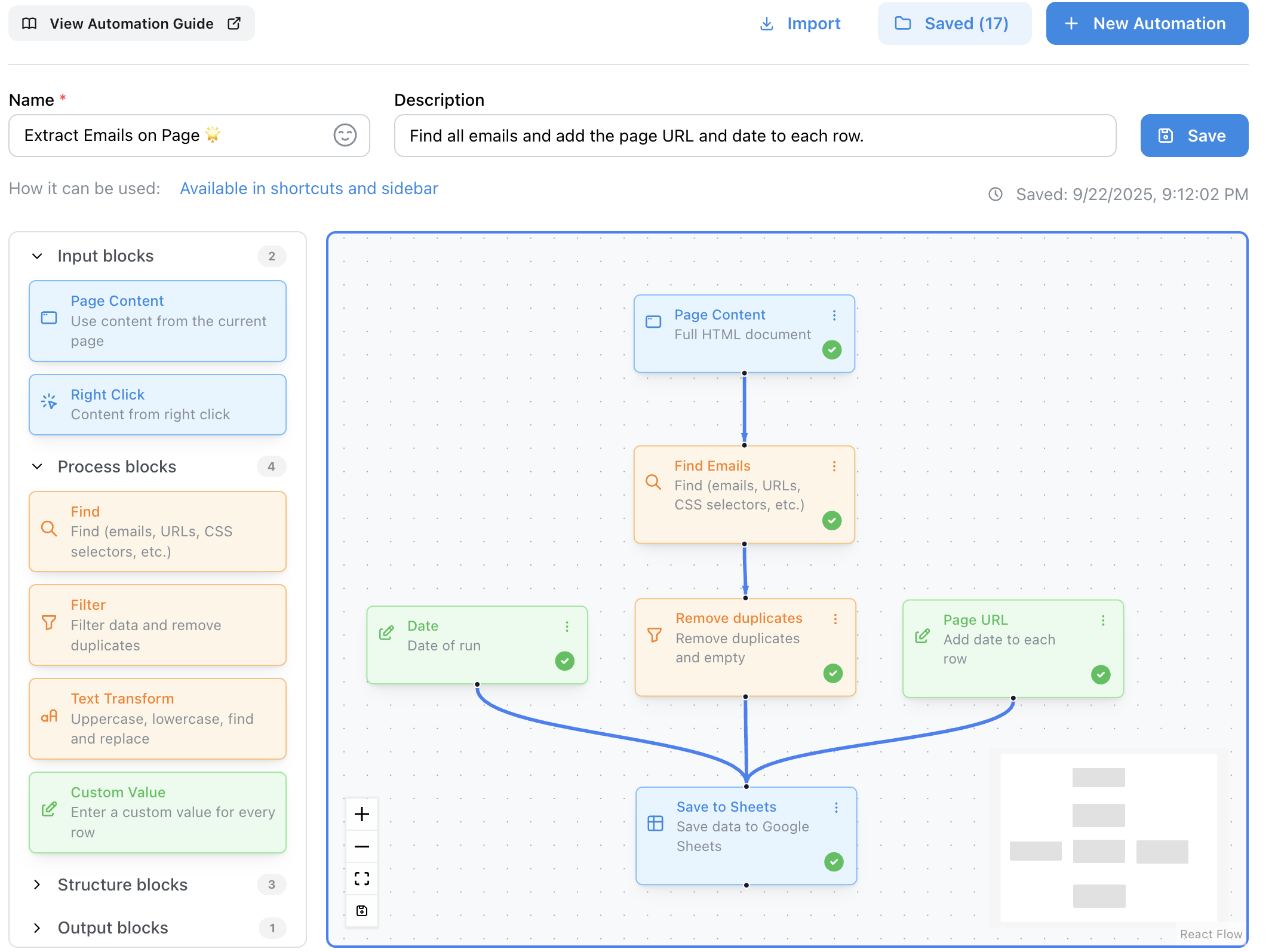
The visual automation builder with input, process, and output blocks — including Custom Value
What makes this especially powerful is the Custom Value block. Custom Values let you inject additional data into every row your automation saves — metadata that gives AI formulas more context to work with.
What Custom Values Can Add
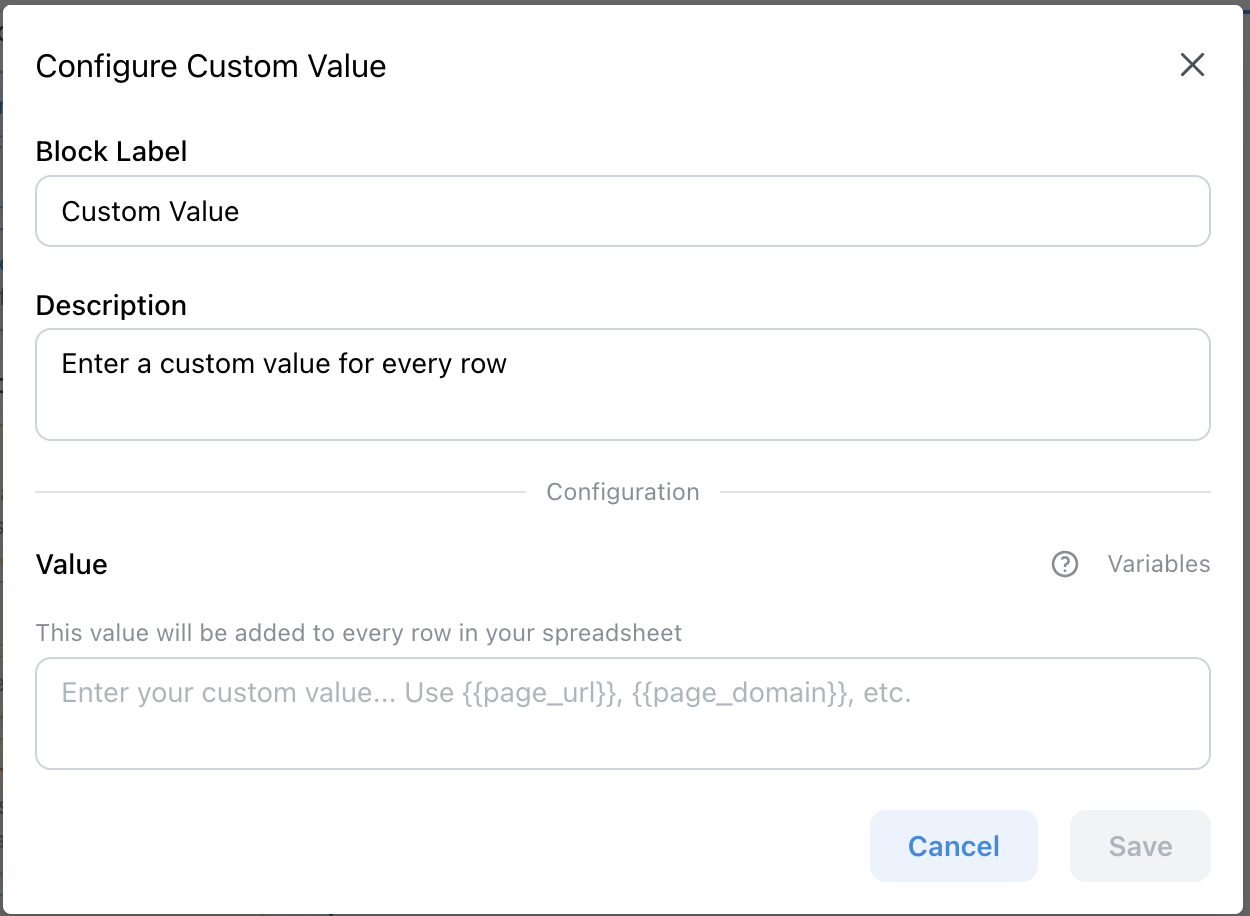
The Custom Value block supports manual text, Sheets formulas, and page variables like {{page_url}}
Custom Values support four types of input:
- Manual text — Add fixed labels, categories, or notes (e.g., “LinkedIn Lead”, “Competitor Product”)
- Google Sheets formulas — Use
=TODAY(),=NOW(), or=RAND()to timestamp or tag rows automatically - Page variables —
{{page_url}},{{page_domain}}, and{{page_path}}capture source info from the page you’re on - Multi-line text — Add longer context, criteria, or instructions
Example: Automated Lead Pipeline
Here’s how Automations + Custom Values + AI formulas work together for LinkedIn prospecting:
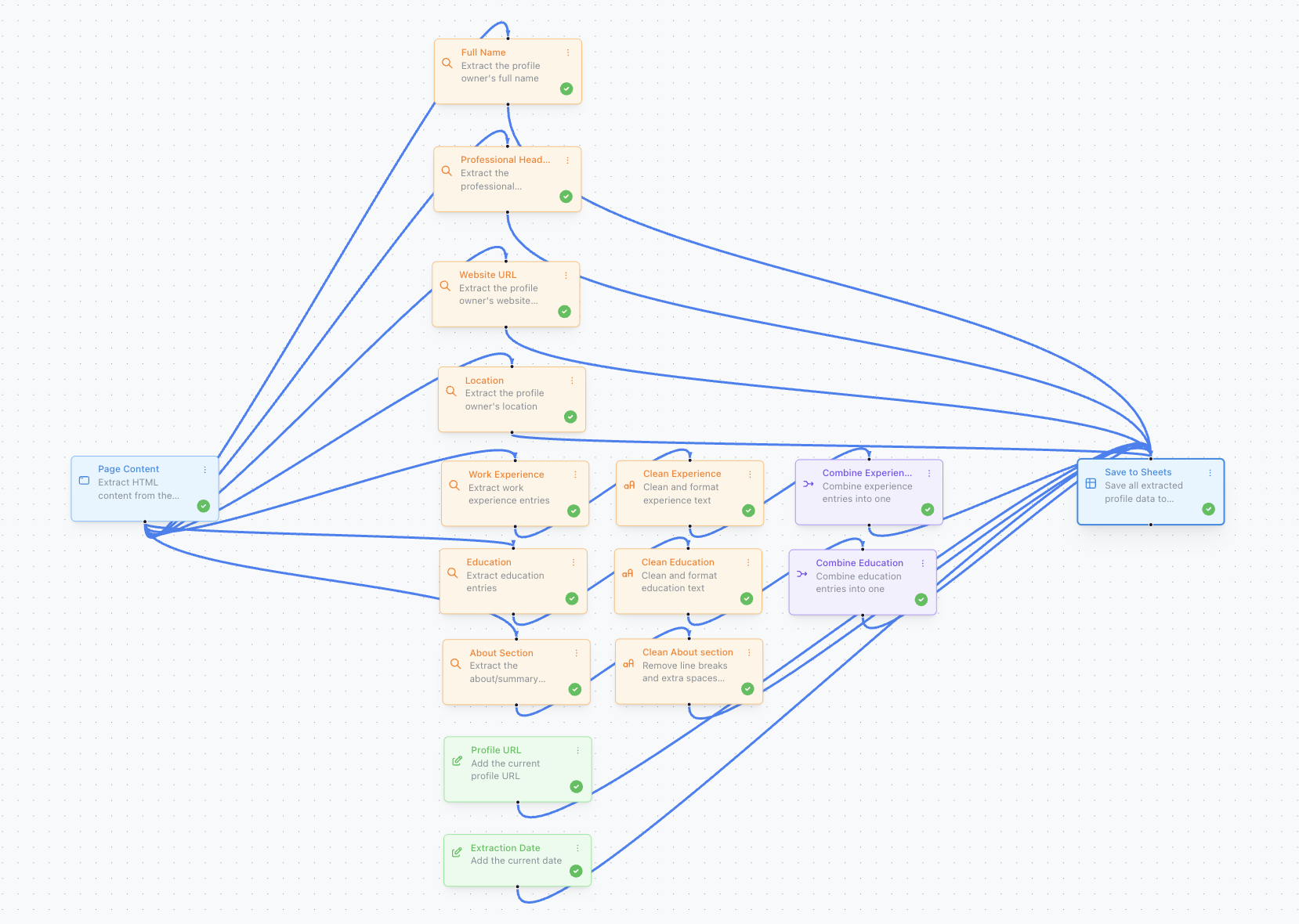
The LinkedIn Profile automation extracts complete profile data with a single click or keyboard shortcut
The Automation extracts:
- Name, Headline, About section, Experience (from the profile page using Find blocks)
Custom Value blocks add:
{{page_url}}→ Profile URL column (automatically captured)=TODAY()→ Date Added column (auto-timestamped)"LinkedIn"→ Source column (fixed label)
AI formulas process the result:
| Name | Headline | About | URL | Date | Source | Industry | Priority |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jane Smith | VP Marketing at Acme | 15 years in B2B… | [auto] | [auto] | =AI(“industry?”, C2) | =AI(“priority for selling dev tools: high/med/low?”, B2:C2) |
One click or keyboard shortcut runs the automation. The Custom Values add the metadata. The AI formulas evaluate the lead. You go from visiting a profile to having a fully qualified, timestamped, sourced row — without touching a single cell.
Example: Multi-Source Product Research
Track products across Amazon, eBay, and Etsy with automations that tag the source automatically:
Custom Value blocks add:
{{page_domain}}→ Source column (captures “amazon.com”, “ebay.com”, or “etsy.com” automatically)=TODAY()→ Date Checked column
AI formulas compare across sources:
=AI("is this a good deal compared to typical pricing?", A2:C2)— the AI sees product name, description, and price together, and can factor in which platform it came from because{{page_domain}}captured the source
Example: Timestamped Content Monitoring
For tracking Reddit discussions or news articles over time:
Custom Value blocks add:
{{page_url}}→ Source URL{{page_path}}→ Subreddit or section path=TODAY()→ Date Captured
AI formulas analyze trends:
- Sentiment analysis on each captured post
- Topic classification using the page path as additional context
=AI("has sentiment shifted since last week? compare to previous rows", B2)— the timestamps from=TODAY()let you track changes over time
Why This Matters
Without Custom Values, you’d need to manually type the URL, the date, and the source label for every row. With them, the automation captures that context silently. And that context is exactly what makes AI formulas more accurate — they can factor in where the data came from, when it was captured, and what category it belongs to.
The LinkedIn Profile automation template and LinkedIn Job Post automation are ready-made starting points. Add Custom Value blocks for metadata, set up AI formula columns, and you have a fully automated data pipeline.
Getting Started
- Check your Google account — You need an eligible Google Workspace or Google AI plan to use
=AI()formulas. Check Google’s requirements here. - Set up your sheet — Create columns for the raw data you’ll save, plus columns with
=AI()formulas for processing. - Install Add to Sheets — Get the extension and configure your columns.
- Start saving — Use right-click save or Quick Row Entry to get data into your sheet. Watch the AI columns fill in automatically.
Related Guides
- Quick Row Entry for Google Sheets — The form-based entry that pairs with AI formulas
- No-code Automations — Automate data extraction before AI processes it
- Save LinkedIn Profiles to Google Sheets — Lead qualification workflow
- Save Amazon Products to Google Sheets — Product research workflow
- Save Indeed Jobs to Google Sheets — Job fit analysis workflow
Ready to automate your data processing?
Install Add to Sheets for Chrome — it’s free. Upgrade to Pro for Quick Row Entry and unlimited columns.